编译器
在设计思路和原理中,我们简单说了一下Mars中是如何将Vue模版编译成小程序的 .wxml、.css、.js以及.json文件,本章我们具体讲述一下编译器具体的相关内容。
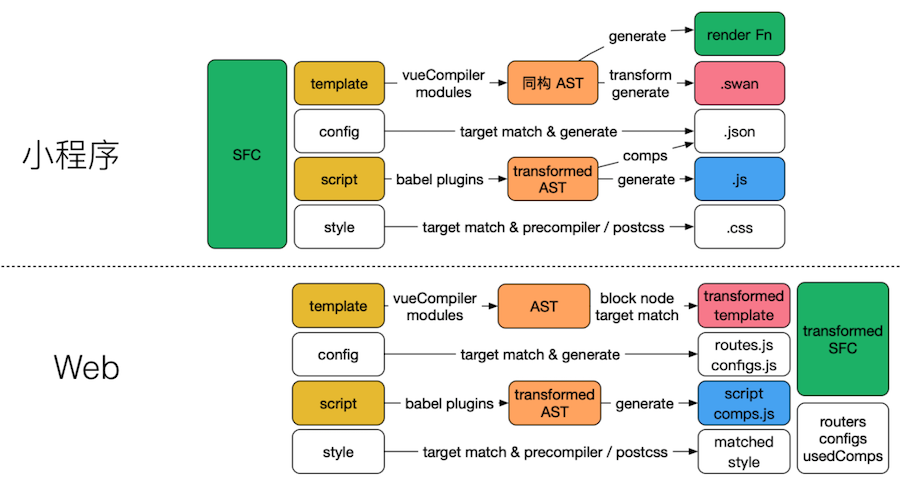
编译器目录结构
在Mars源码中mars-build是编译器相关部分的源码,我们看一下其目录结构:
├── compiler
| ├── file # 文件编译器
| ├── runtime # 运行时编译器
| ├── script # JS 编译器
| ├── sfc # SFC 编译器
| ├── style # CSS 编译器
| └── template # template 编译器
├── helper
| ├── babel # babel辅助配置
| ├── config # 文件后缀配置
| ├── html-parser # HTML 解析器
| ├── log # 日志打印
| ├── path # 路径处理工具
| └── util # 其他工具类
├── h5
| └── transform # H5 转换器
├── swan
| └── transform # 百度小程序转换器
├── wx
| └── transform # 微信小程序转换器
├── scripts
| ├── defaultConfig # 工程默认配置文件
| ├── getConfig # 获取并解析工程配置
| ├── gulpTasks # 编译任务
| └── run # 编译器执行入口
├── gulp-mars-base # 公共的编译任务文件
├── gulp-mars-h5 # H5 的编译任务文件
├── gulp-mars-swan # 百度小程序的编译任务文件
├── gulp-mars-wxml # 微信小程序的编译任务文件
└── index.js # 入口文件,暴露四个函数(build、clean、watch、getConfig)编译执行流程
编译过程整体的执行流程如下:
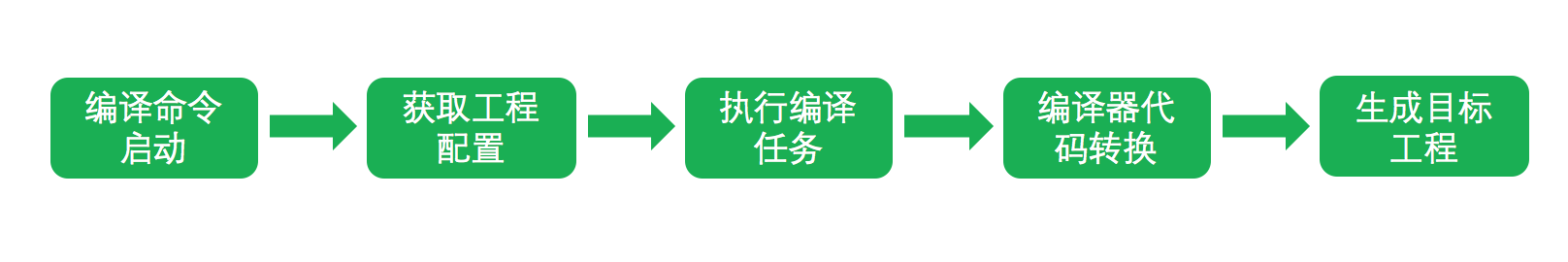
然后我们看一下它是怎么实现的。
编译命令启动
package.json 启动命令
我们从项目入口 package.json 一步步看一下编译命令启动的过程:
"scripts": {
"serve": "mars serve",
"build": "mars build",
"build:h5": "mars build -t h5",
"build:wx": "mars build -t wx",
"serve:h5": "mars serve -t h5",
"serve:wx": "mars serve -t wx"
},当我们执行 npm run serve:wx 将会在本地起一个 serve,用于将工程 src 下的 .vue 文件编译成微信小程序的工程 dist-wx。执行 npm run serve:wx 实际会执行 mars serve -t wx。package.json 中的 scripts 对象的键值对,类似于在工程中注册一些启动脚本,类似于 gulp 的 task 命令。如果本地 node_modules 下的 .bin 下有相关的命令文件,会默认找这里的命令,如果没有会去找全局安装的命令,类似于 webpack 可以全局安装,也可以在项目中单独安装,这里我们的 mars 是全局安装 mars-cli 注册的命令。
@mars/cli 命令行工具
@mars/cli 提供了类似 @vue/cli 工具的功能,提供了初始化项目、CLI 服务、依赖升级、获取运行环境信息等基本功能。
mars create [options] <app-name> # 初始化项目,如创建的项目不需要支持 h5,选择 `仅小程序` 否则,若需要支持 h5,选择 `小程序和 H5`;
mars serve [options] # 开发项目,可通过 `-t` 设置编译目标,可选值为 `swan` | `wx` | `h5`,默认 `wx`;
mars build [options] # 构建项目(用于上线),可通过 `-t` 设置编译目标,可选值为 `swan` | `wx` | `h5`,默认 `wx`;
mars update [options] # 升级当前项目 @mars 相关依赖库
mars info # 获取运行环境信息mars-cli 包 bin/mars.js 中通过 commander 注册命令。
const program = require('commander');
program
.version(getCliVersion())
.usage('<command> [options]');
program
.command('create <app-name>')
.description('create a new project')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-f, --force', 'Overwrite target directory if it exists')
.action(async (name, cmd) => {});
program
.command('build')
.description('build project in production mode')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-t, --target <target>', 'Build target (swan | h5 | wx, default: swan)')
.option('-w, --watch', 'Open watch mode')
.option('--h5skip <process>', 'Skip h5 compile process (mars | vue)')
.action(cmd => {});
program
.command('serve')
.description('serve project in development mode')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-t, --target <target>', 'Build target (swan | h5 | wx, default: swan)')
.option('--h5skip <process>', 'Skip h5 compile process (mars | vue)')
.action(cmd => {});
program
.command('update')
.description('update all mars dependences')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-f, --force', 'Force update all denpenences to latest version')
.action(cmd => {});
program
.command('info')
.description('Diagnostics Mars env info')
.action(cmd => {});
program
.arguments('<command>')
.action(cmd => {});
program.on('--help', () => {});
program.commands.forEach(c => c.on('--help', () => console.log()));
program.parse(process.argv);create 指令:
create 指令直接执行了 vue-cli 中的 create 方法:
program
.command('create <app-name>')
.description('create a new project')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-f, --force', 'Overwrite target directory if it exists')
.action(async (name, cmd) => {
const options = cleanArgs(cmd);
if (minimist(process.argv.slice(3))._.length > 1) {
console.log(chalk.yellow('\n Info: You provided more than one argument. '
+ 'The first one will be used as the app\'s name, the rest are ignored.'));
}
const inquirer = require('inquirer');
const {target} = await inquirer.prompt([
{
name: 'target',
type: 'list',
message: '选择创建项目类型:',
choices: [
{
name: '小程序和 H5',
value: 'h5'
},
{
name: '仅小程序',
value: 'noH5'
}
]
}
]);
let needPWA = false;
if (target !== 'noH5') {
let res = await inquirer.prompt([
{
name: 'target',
type: 'list',
message: 'H5 是否需要支持 PWA:',
choices: [
{
name: '不需要',
value: 'no'
},
{
name: '需要',
value: 'need'
}
]
}
]);
needPWA = res.target === 'need';
}
/* eslint-disable fecs-camelcase */
options.inlinePreset = JSON.stringify({
useConfigFiles: false,
router: false,
useEslint: false,
_isPreset: true,
plugins: {
'@marsjs/cli-template': {
version: '^0.3.0',
noH5: target === 'noH5',
needPWA
}
}
});
/* eslint-enable fecs-camelcase */
if (!options.registry) {
options.registry = defaultConfig.registry;
}
const create = require('@vue/cli/lib/create');
await create(name, options);
// 把 @vue/cli-service 生成的文件都删除
const basePath = path.resolve(process.cwd(), './' + name);
const globby = require('globby');
let files = await globby([
'**/*',
'!node_modules',
'!mars',
'!package.json',
'!package-lock.json'
], {cwd: basePath, deep: false, onlyFiles: false});
for (const rawPath of files) {
await fs.remove(basePath + '/' + rawPath);
}
files = await globby(['**/*'], {cwd: basePath + '/mars', deep: false, onlyFiles: false});
for (const rawPath of files) {
await fs.move(basePath + '/mars' + '/' + rawPath, basePath + '/' + rawPath);
}
fs.remove(basePath + '/mars');
});因此整个执行流程与 vue-cli 是相同的。
文件产出使用了单独的库,@mars/cli-template 作 vue-cli 的插件。由于 vue-cli 默认一定会加载 @vue/cli-service 这个插件,产出了大量无用内容,因此在 create 完成后,对无用文件进行了删除。
执行 create 命令时,提示用户选择创建的项目是否需要支持 h5,之后修改 preset,将参数传给 @mars/cli-template。@mars/cli-template 会根据参数 render 不同的文件内容。目录如下:
├── bin
├── generator
| ├── dist-h5
| ├── template
| ├── template-h5
| └── template-pwa- mars-cli-template/generator/template: 基础项目文件,无论是否支持 H5,都会使用;
- mars-cli-template/generator/template-h5: 当项目需要支持 h5 时,会在 template 的基础上增加 template-h5 的内容;
除此之外,还有一个 dist-h5 文件夹,这个文件夹为产出 vue 工程所需要的一些文件,不需通过 vue-cli 的 generator 进行 render,直接进行文件拷贝。拷贝发生在每次执行 h5 编译时,判断文件不存在时进行拷贝。
serve 指令:
上述我们在应用工程中 serve 命令,实质是启动 @mars/cli 的命令。我们以 mars serve 为例说明 @mars/cli 的基本工作原理。
//mars.js
program
.command('serve')
.description('serve project in development mode')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-t, --target <target>', 'Build target (swan | h5 | wx, default: swan)')
.option('--h5skip <process>', 'Skip h5 compile process (mars | vue)')
.action(cmd => {
//将cmd参数转换成对象,{target:wx}
const options = cleanArgs(cmd);
const buildPath = path.resolve(__dirname, './mars-serve.js');
//将targets多个转换成数组
const targets = (options.target || 'swan').split(',');
targets.forEach(t => {
//脚本参数
const args = [buildPath, '-t', t];
Object.keys(options).forEach(op => {
if (op === 'target') {
return;
}
//如果有别的参数,就将其加入到args中
if (options[op] !== false) {
args.push('--' + op);
if (options[op] !== true) {
args.push(options[op]);
}
}
});
execa('node', args, {
stdout: 'inherit',
stderr: 'inherit'
});
});
});我们可以看到它会先将cmd参数转换成对象形式,然后再组装buildPath脚本命令的参数,最终会使用execa调用node执行mars-serve.js文件。
//mars-serve.js
program
.description('serve project in development mode')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-t, --target <target>', 'Build target (swan | h5 | wx, default: swan)')
.option('--h5skip <process>', 'Skip h5 compile process (mars | vue)')
.action(cmd => {
const start = require('../lib/serve');
const options = cleanArgs(cmd);
if (!options.registry) {
options.registry = defaultConfig.registry;
}
start(options);
})
.parse(process.argv);在 bin/mars-serve.js中判断如果没设置registry仓库镜像则会提供一个默认的值,然后会调用 lib/serve.js的start方法。
const {error, stopSpinner} = require('@vue/cli-shared-utils');
const execa = require('execa');
const {getConfig} = require('./scripts/getConfig');
async function start(cmd) {
const {target, buildPath, env} = getConfig(cmd);
const {
watch,
clean,
getConfig: getBuildConfig
} = require(buildPath);
const options = {
target,
env
};
if (!process.env.NODE_ENV) {
process.env.NODE_ENV = 'development';
}
process.env.MARS_CLI_OPTIONS = JSON.stringify(options);
process.env.MARS_CLI_TARGET = target;
process.env.MARS_CLI_ENV = env;
// process.env.MARS_CLI_DEST = env ? `./dist-${env}` : './dist-h5';
process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET = `${target}${env ? `:${env}` : ''}`;
const {dest, h5: h5Config} = getBuildConfig(options);
const servePath = dest.servePath;
// for mars-cli-service
process.env.MARS_PWA = !!(h5Config && h5Config.supportPWA);
function serveH5() {
// const child = execa('npm', ['run', 'serve-dist-h5']);
const args = ['mars-cli-service', 'serve', '--path', servePath];
console.log('[serve h5]', args.join(' '));
const child = execa('npx', args);
child.stdout.pipe(process.stdout);
child.stderr.pipe(process.stderr);
}
if (target === 'h5' && cmd.h5skip === 'mars') {
return serveH5();
}
clean(options).once('stop', () => {
watch(options).once('stop', () => {
console.log(`[serve ${target}]`, 'watching...');
if (target === 'h5' && cmd.h5skip !== 'vue') {
serveH5();
}
});
});
}
module.exports = (...args) =>
start(...args).catch(err => {
stopSpinner(false); // do not persist
error(err);
if (!process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST) {
process.exit(1);
}
});其中getConfig 的实现如下:
// 获取target参数 h5:pc / swan:xx
function getTargetParam(target = 'swan') {
let params = target.split(':');
return {
target: params[0],
param: params[1]
};
}
function getConfig(cmd) {
const {
target,
param: env
} = getTargetParam(cmd.target);
const buildPath = path.resolve(process.cwd(), 'node_modules/@marsjs/build');
return {
target,
buildPath,
env
};
}在start方法中调用了getConfig来获取编译器的路径和编译的目标平台,然后通过require导入编译器对外暴露的clean、watch、getConfig方法,然后给环境变量赋值MARS_CLI_OPTIONS和MARS_CLI_TARGET后面会用到,通过getConfig配置获取编译后的目录以及h5的相关配置,最后调用clean和watch方法来运行和监听。
如果是h5的话编译需要两步,小程序项目会通过 mars-build 先编译为 vue 工程,之后需要使用 vue-cli-service 对 vue 工程进行编译。我们可以看到其serverH5执行了mars-cli-service,mars-cli-service 实际引用了 @vue/cli-service/lib/Service,对小程序转换出的 vue 项目进行编译。
我们大体看一下mars-cli-service的内容:
(async () => {
const baseConfigPath = process.cwd() + '/vue.config.js';
if (!fs.existsSync(baseConfigPath)) {
console.error(chalk.red('vue.config.js 文件未找到,请确认当前所在工程支持编译到 h5。'));
}
if (!process.env.VUE_CLI_SERVICE_CONFIG_PATH) {
const env = process.env.MARS_CLI_ENV;
const envConfigPath = env && `${process.cwd()}/vue.config.${env}.js`;
const configPath = envConfigPath && fs.existsSync(envConfigPath)
? envConfigPath
: baseConfigPath;
process.env.VUE_CLI_SERVICE_CONFIG_PATH = configPath;
}
// await fs.copy(process.cwd() + '/vue.config.js', context + '/vue.config.js');
let pwaSupport = false;
try {
pwaSupport = JSON.parse(process.env.MARS_PWA);
}
catch (e) {}
const plugins = pwaSupport
? [
idToPlugin('@marsjs/vue-cli-plugin-mars-web'),
idToPlugin('@vue/cli-plugin-babel'),
idToPlugin('@marsjs/vue-cli-plugin-pwa')
]
: [
idToPlugin('@marsjs/vue-cli-plugin-mars-web'),
idToPlugin('@vue/cli-plugin-babel')
];
const service = new Service(context, {
plugins
});
service.run(command, args, rawArgv).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
process.exit(1);
});
})();build指令
build指令和serve大体类似,我们直接看调用的lib/build.js文件
async function build(cmd) {
const {target, buildPath, env} = getConfig(cmd);
const {
build,
watch,
clean,
getConfig: getBuildConfig
} = require(buildPath);
const options = {
target,
env
};
if (!process.env.NODE_ENV) {
process.env.NODE_ENV = 'production';
}
process.env.MARS_CLI_OPTIONS = JSON.stringify(options);
process.env.MARS_CLI_TARGET = target;
process.env.MARS_CLI_ENV = env;
// process.env.MARS_CLI_DEST = env ? `./dist-${env}` : './dist-h5';
process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET = `${target}${env ? `:${env}` : ''}`;
const {dest, h5: h5Config} = getBuildConfig(options);
const servePath = dest.servePath;
// for mars-cli-service
process.env.MARS_PWA = !!(h5Config && h5Config.supportPWA);
function serveH5() {
// const child = execa('npm', ['run', 'build-dist-h5']);
const args = ['mars-cli-service', 'build', '--path', servePath];
console.log('[build h5]', args.join(' '));
const child = execa('npx', args);
child.stdout.pipe(process.stdout);
child.stderr.pipe(process.stderr);
}
if (target === 'h5' && cmd.h5skip === 'mars') {
return serveH5();
}
const run = cmd.watch ? watch : build;
clean(options).once('stop', () => {
run(options).once('stop', () => {
console.log(`[build ${target}]`, cmd.watch ? 'watching...' : 'done!');
if (target === 'h5' && cmd.h5skip !== 'vue') {
serveH5();
}
});
});
}它相比serve多引入了build方法。
获取工程配置
@mars/build 入口文件 index.js 对外暴漏了 build、clean、watch、getConfig 四个方法,我们先看一下 getConfig 方法的实现。
//src/scripts/getConfig.js:
/**
* getConfig
*
* @param {mars.options} options options
* @return {mars.config}
*/
function getConfig(options) {
if (!options && process.env.MARS_CLI_OPTIONS) {
try {
options = JSON.parse(process.env.MARS_CLI_OPTIONS);
}
catch (e) {}
}
if (!options) {
throw new Error('pass options to @marsjs/build or use @marsjs/cli');
}
return formatConfig(options);
}
// 兼容原 Task 的配置格式
function formatConfig(options) {
//获取目标平台,例如wx
const target = options.target;
const targetEnv = process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET || target;
let config = getProjectConfig(targetEnv);
config = merge(getDefaultConf(targetEnv), config);
const destPath = config.dest;
config.dest = {
path: destPath,
coreDir: 'mars-core'
};
if (target === 'h5') {
const servePath = destPath.replace(':', '-').replace(/\/src$/, '');
config.dest.path = servePath + '/src';
config.dest.servePath = servePath;
}
config.source = {
sfc: config.source,
assets: config.assets
};
config.options = {
sfc: config.options
};
config = merge(config, getRuntimeConfig(config.devConfig || {}));
// init px2units.options.multiple
// 规定 H5 中 1rem = 100px
const {designWidth, modules} = config;
if (designWidth && modules.postcss.px2units) {
const multiple = target === 'h5' ? .5 / 100 : 1;
modules.postcss.px2units = Object.assign({
targetUnits: target === 'h5' ? 'rem' : 'rpx',
multiple: multiple * 750 / designWidth
}, modules.postcss.px2units);
}
return config;
}
function getProjectConfig(target) {
let projectConfig = {};
const configPath = path.resolve(process.cwd(), './mars.config.js');
if (fs.existsSync(configPath)) {
projectConfig = require(configPath)(target);
}
return projectConfig;
}在getConfig中我们拿到从serve或build脚本传递过来的参数,如果没有的话我们通过process.env.MARS_CLI_OPTIONS环境变量的值来获取。然后调用formatConfig获取配置。
formatConfig中会通过getProjectConfig拿到项目根目录下mars.config.js的值。示例如下:
//mars.config.js
module.exports = function (target) {
const config = {
h5: {
navigationBarHomeColor: 'light',
showNavigationBorder: true,
mode: 'hash',
useTransition: true
},
postprocessors: {
postcss: {
options: {
plugins: [
require('autoprefixer')({
overrideBrowserslist: ['iOS >= 7', 'android >= 2.3']
})
]
}
}
}
};
return config;
};然后通过getDefaultConf拿到编译库中的默认配置与项目根目录下配置合并生成新配置。默认配置如下
//src/scripts/defaultConfig.js:
module.exports = function (target) {
const CLI_TARGET = process.env.MARS_CLI_TARGET || target;
const config = {
verbose: false,
projectFiles: ['project.swan.json', 'project.config.json'],
source: ['src/**/*.vue'],
dest: `./dist-${target}`,
assets: CLI_TARGET === 'h5' ? [
'src/**/*.!(vue|swan|wxml)'
]
: [
'src/**/*.!(vue)'
],
designWidth: 750,
watch: ['src/**/*'],
framework: {},
modules: {
postcss: {
px2units: {
targetUnits: CLI_TARGET === 'h5' ? 'rem' : 'rpx'
}
}
},
preprocessors: {
less: {
extnames: ['less']
},
sass: {
extnames: ['sass', 'scss']
},
stylus: {
extnames: ['stylus', 'styl']
},
typescript: {
extnames: ['ts']
}
},
postprocessors: {
postcss: {
extnames: ['css', 'less', 'sass', 'scss', 'stylus', 'styl'],
options: {
plugins: [require('autoprefixer')]
}
}
}
};
return config;
};然后通过getRuntimeConfig将运行时的配置合并到配置中。
//src/scripts/getConfig.js:
function getRuntimeConfig({
corePath = './node_modules/@marsjs/core'
}) {
return {
source: {
runtime: corePath + '/src/**/*.js',
h5Template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../h5/template/**/*.@(vue|js|css)')
},
options: {
sfc: {}
}
};
}在serve和build命令行中只需要获取config的dest和h5config即可。
执行编译任务
在mars-cli中我们看到serve和build执行最后调用了mars-build的clean、build、watch方法。方法定义如下:
//src/scripts/run.js:
function clean(options = {}) {
const config = getConfig(options);
const taskClean = getTaskClean(config, options);
// gulp.task('clean', );
log.info('[start task]', 'clean');
return taskWrapper(taskClean)();
// return gulp.start('clean');
}
/**
* build
*
* @param {mars.buildOptions} options options
* @return {Object}
*/
function build(options = {}) {
const config = getConfig(options);
const buildTasks = getBuildTasks(config, options);
// gulp.task('build', buildTasks);
log.info('[start task]', 'build');
return taskWrapper(buildTasks)();
// return gulp.start('build');
}
function watch(options = {}) {
const config = getConfig(options);
const {watch: watchConfig} = config;
const buildTasks = getBuildTasks(config, options);
log.info('[start task]', 'build && watch');
gulp.watch(watchConfig, buildTasks);
return taskWrapper(buildTasks)();
// return gulp.start('watch');
}watch、build、clean 方法各自启动了task任务,分别是getTaskClean和getBuildTasks,我们看一下其定义:
//src/scripts/gulpTasks.js
/**
* getTaskClean
*
* @param {mars.config} config config
* @param {mars.options} options options
* @return {Function}
*/
function getTaskClean(config, options) {
const {projectFiles} = config;
// clean servePath for h5
const dest = config.dest.path;
// let dest = config.dest.servePath || config.dest.path;
return callback => {
let files = [`${dest}/**`, `!${dest}`].concat(projectFiles
? (projectFiles.map(item => `!${dest}/${item}`))
: []);
return del(files, callback);
};
}getTaskClean主要是调用del库对编译后的目录进行清理。
//src/scripts/run.js
/**
* getBuildTasks
*
* @param {mars.config} config config
* @param {mars.options} options options
* @return {string[]}
*/
function getBuildTasks(config = {}, options = {}) {
const {target} = options;
// config = formatConfig(config);
gulp.task('compile:sfc', getTaskSFC(config, options));
gulp.task('copy:assets', getTaskCompileAssets(config, options));
let buildTasks = [
'compile:sfc',
'copy:assets'
];
// if (target !== 'h5') {
gulp.task('compile:runtime', getTaskRuntime(config, options));
buildTasks.push('compile:runtime');
// // }
return gulp.parallel(buildTasks.map(t => gulp.task(t)));
// return buildTasks;
}getBuildTasks中定义了gulp任务,包括编译sfc、复制assets资源,编译runtime运行时。那么我们总算知道了Vue编译成小程序主要是通过定义了这几个gulp任务来执行的。
其中最主要的是getTaskSFC、getTaskCompileAssets、getTaskRuntime这三个任务的定义。我们接下来仔细分析这三个Task。
SFC 编译任务
我们先看一下SFC是如何编译的,找到getTaskSFC的代码如下:
/**
* getTaskSFC
*
* @param {mars.config} config config
* @param {mars.options} options options
* @return {Function}
*/
function getTaskSFC(config, options) {
const {dest: buildDest, source} = config;
const dest = config.dest.path;
const {target} = options;
let compileOption = config.options.sfc;
compileOption = Object.assign({
dest,
target,
coreDir: buildDest.coreDir
}, compileOption);
compileOption._argv = options;
compileOption._config = config;
let compile;
if (target === 'swan') {
compile = require('../gulp-mars-swan');
}
if (target === 'wx') {
compile = require('../gulp-mars-wxml');
}
if (target === 'h5') {
compile = require('../gulp-mars-h5');
compileOption.commit = (type, key, val) => {
h5Configs[type][key] = val;
};
// for packages
if (config.packages) {
const {api, components} = config.packages;
compileOption.devApiPath = api;
compileOption.devCompPath = components;
}
}
if (!compile) {
throw new Error('[getTaskSFC] cannot find compiler match target ' + target);
}
const changedOptions = target !== 'h5' ? {
extension: '.js'
} : {};
const logger = config.verbose ? log.info : log.write;
return () => {
if (!source.sfc || (Array.isArray(source.sfc) && source.sfc.length === 0)) {
return Promise.resolve('[warning] empty sfc globs');
}
return gulp.src(source.sfc, {allowEmpty: true})
.pipe(changed(dest, changedOptions))
.pipe(intercept(file => {
file.isBuffer() && logger('[compile:sfc]:', getPathToCWD(file.path));
return file;
}))
.pipe(compile(compileOption));
};
}在这段代码中它主要做了这么几件事:
- 获取SFC编译需要的配置,主要包括编译后的目录、SFC源码路径、编译目标小程序、编译的运行时目录
source: {
sfc: [ 'src/**/*.vue' ],
assets: [ 'src/**/*.!(vue)' ],
runtime: './node_modules/@marsjs/core/src/**/*.js',
}- 引入并获取编译器,微信则调用gulp-mars-wxml、百度调用gulp-mars-swan。
- 通过gulp.src读取SFC源码,然后通过pipe管道的方式来处理源码,即调用gulp-mars-wxml来编译
最终会调用gulp-mars-wxml.js来编译,接下来我们看一下整个流程。
编译入口
gulp-mars-wxml.js是小程序编译的入口,其内容如下:
//src/gulp-mars-wxml.js
const {gulpPlugin} = require('./gulp-mars-base');
const {
getCompiler,
generate,
mark
} = require('./compiler/template/index');
const {transform} = require('./wx/transform/index');
const templateCompiler = getCompiler(mark, transform, generate, 'wx');
const styleCompiler = require('./compiler/style/style').compile;
const scriptCompiler = require('./compiler/script/script').compile;
const scriptPostCompiler = require('./compiler/script/script').postCompile;
const configCompiler = require('./compiler/script/config').compile;
const {FILE_SUFFIX} = require('./helper/config');
const compilers = {
templateCompiler,
styleCompiler,
scriptCompiler,
scriptPostCompiler,
configCompiler
};
// 导出插件主函数
module.exports = function (opt) {
const target = 'wx';
opt.fileSuffix = FILE_SUFFIX[target];
opt.target = target;
return gulpPlugin(opt, compilers);
};我们可以看到小程序编译入口文件中定义了一系列编译器
- templateCompiler
- styleCompiler
- scriptCompiler
- scriptPostCompiler
- configCompiler
这些与SFC 编译相关的 compiler 都会被传到 gulp-mars-base.js 的 gulpPlugin 这个方法:
//src/gulp-mars-base.js
const {parse: sfcParser} = require('./compiler/sfc/parser');
const {compile: sfcCompiler} = require('./compiler/sfc/compiler');
const log = require('./helper/log');
async function compile(file, opt, compilers) {
const {
target = 'swan',
fileSuffix = {
html: 'swan',
js: 'js',
css: 'css',
json: 'json'
}
} = opt;
const rPath = path.relative(file.base, file.path);
let fPath = slash(path.resolve(file.cwd, opt.dest, rPath).replace(/\.vue$/, ''));
let baseName = path.basename(fPath);
const isApp = baseName.toLowerCase() === 'app';
if (isApp && baseName === 'App') {
file.path = file.path.replace('App.vue', 'app.vue');
fPath = fPath.replace('App', 'app');
baseName = 'app';
}
let coreRelativePath = path.join(
path.relative(
path.parse(fPath).dir,
path.resolve(file.cwd, opt.dest)
) || '.',
opt.coreDir || 'common'
);
coreRelativePath = coreRelativePath[0] === '.' ? coreRelativePath : './' + coreRelativePath;
coreRelativePath = slash(coreRelativePath + '/index');
let fileDirPath = fPath.replace(/[^/]+$/, '');
try {
mkdirp.sync(fileDirPath);
}
catch (e) {}
const options = Object.assign({
isApp,
coreRelativePath,
compilers,
fileSuffix,
fPath,
baseName
}, opt);
const sfcFile = sfcParser(file, options);
return sfcCompiler(sfcFile, options);
}
function gulpPlugin(opt = {dest: './dist'}, compilers) {
const stream = through.obj(function (file, enc, cb) {
if (file.isStream()) {
this.emit('error', new PluginError(PLUGIN_NAME, 'Streams are not supported!'));
return cb();
}
if (file.isBuffer()) {
compile(file, opt, compilers)
.then(_ => cb(null, file))
.catch(err => {
log.error('[COMPILE ERROR]:', err);
cb(null, file);
});
}
});
return stream;
}在gulpPlugin中调用compile方法,并将compilers编译器传递进去。在compile方法中,补充相关配置内容:
{
isApp: false,
coreRelativePath: '../../mars-core/index',
compilers: {
templateCompiler: [Function: compiler],
styleCompiler: [Function: compile],
scriptCompiler: [AsyncFunction: compile],
scriptPostCompiler: [AsyncFunction: postCompile],
configCompiler: [Function: compile]
},
fileSuffix: { html: 'wxml', js: 'js', css: 'wxss', json: 'json' },
fPath: 'C:/Users/18307/Desktop/Mars/packages/demo/dist-wx/pages/home/index',
baseName: 'index',
}然后调用sfcParser将SFC解析成四段式:
{
script: '',
styles: '',
template: '',
config: ''
}最终将解析后的内容传递给sfcCompiler进行编译。我们接下来分别看看sfcParser和sfcCompiler做了哪些内容。
解析 SFC 文件
我们打开sfcCompiler文件看一下,找到它位于src/compiler/sfc/compiler.js中导出的parse函数。
//src/compiler/sfc/compiler.js
const File = require('./File');
const {parseHTML} = require('../../helper/html-parser');
const {parseComponent} = require('vue-template-compiler/build');
// const merge = require('lodash.merge');
const merge = require('../../helper/util').merge;
/**
* pre parse SFC content to convert <script type="config"> => <config>
*
* @description since vue-template-compiler parseComponent takes only one <script> block
* @param {string} content SFC content
* @return {string}
*/
function preParse(content) {
let blocks = [];
let depth = 0;
let currentBlock = null;
function start(tag, attrs, unary, start, end) {
if (depth === 0) {
if (
tag === 'script'
&& attrs.find(attr => attr.name === 'type' && attr.value === 'config')
) {
currentBlock = {
tag,
start
};
blocks.push(currentBlock);
}
}
if (!unary) {
depth++;
}
}
function end(tag, start, end) {
if (depth === 1 && currentBlock) {
currentBlock.end = end;
currentBlock.content = `<config${content.slice(currentBlock.start + 7, currentBlock.end - 9)}</config>`;
currentBlock = null;
}
depth--;
}
parseHTML(content, {
start,
end
});
if (blocks.length === 0) {
return content;
}
return blocks.reduce((prev, item, index) => {
const {
start,
end,
content: blockContent
} = item;
const tailContent = index === blocks.length - 1 ? content.slice(end) : '';
const curContent = prev.content
+ content.slice(prev.end, start)
+ blockContent
+ tailContent;
return {
content: curContent,
end
};
}, {
content: '',
end: 0
}).content;
}
function getLang(block, defaultLang) {
return (block && block.lang) ? block.lang : defaultLang;
}
function parseConfig(blocks = []) {
const configObjs = blocks.map(block => {
let {content} = block;
content = content.trim();
const fnStr = `return ${content};`;
try {
return (new Function(fnStr))();
}
catch (e) {
throw new Error(`config parse error: ${content}`);
}
});
return configObjs.length > 0
? merge.apply(null, configObjs)
: null;
}
function wrapFiles(ret, options) {
const {
fPath,
fileSuffix,
target
} = options;
const {
script,
template,
styles,
config
} = ret;
const scriptFile = new File({
type: 'js',
lang: getLang(script, 'js'),
path: fPath + `.${fileSuffix.js}`,
contents: Buffer.from(script ? script.content : ''),
$options: {
attrs: script ? script.attrs : {}
}
});
const stylesArr = styles.filter(item => !item.attrs
|| (!item.attrs.target || item.attrs.target === (process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET || target))
);
const styleContent = stylesArr.reduce((stylestr, {content}) => `${stylestr}
${content}
`, '');
const styleWithLang = styles.find(item => item.lang);
const styleFile = new File({
type: 'css',
lang: getLang(styleWithLang, 'css'),
path: fPath + `.${fileSuffix.css}`,
contents: Buffer.from(styleContent || ''),
$options: {
attrs: styleWithLang ? styleWithLang.attrs : {}
}
});
const templateFile = new File({
type: 'html',
lang: getLang(template, 'html'),
path: fPath + `.${fileSuffix.html}`,
contents: Buffer.from(template ? template.content : ''),
$options: {
attrs: template ? template.attrs : {}
}
});
const jsonFile = new File({
type: 'json',
path: fPath + `.${fileSuffix.json}`,
$options: {
config
}
});
return {
script: scriptFile,
styles: styleFile,
template: templateFile,
config: jsonFile
};
}
exports.parse = function parse(file, options, withWrap = true) {
const {target} = options;
const content = preParse(file.contents.toString());
let {
script = {},
template = {},
styles = [{}],
customBlocks = []
} = parseComponent(content, {});
let configBlocks = {
default: [],
target: []
};
customBlocks.forEach(block => {
if (block.type === 'config') {
if (!block.attrs.target) {
configBlocks.default.push(block);
}
if (block.attrs.target === (process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET || target)) {
configBlocks.target.push(block);
}
}
});
// target config 覆盖 default config,同一类型后面覆盖前面
const config = parseConfig(configBlocks.default.concat(configBlocks.target));
const ret = {
script,
template,
styles,
customBlocks,
config
};
// for H5
if (!withWrap) {
return ret;
}
return wrapFiles(ret, options);
};parse函数主要做了这么几件事:
- 调用preParse将Vue单文件内容中的
<script type="config">转换成<config>,例如:
<script type="config">
{
config: {
navigationBarTitleText: 'Mars'
}
}
</script>转换成
<config type="config">
{
config: {
navigationBarTitleText: 'Mars'
}
}
</config>- 调用vue-template-compiler的parseComponent函数将vue单文件组件解析为描述符,描述符示例如下:
{
template: {
type: 'template',
content: '\n' +
'<view class="home-wrap">\n' +
' <view class="home-text">Vue 驱动的多端开发框架</view>\n' +
' <Hello></Hello>\n' +
'</view>\n',
start: 10,
attrs: {},
end: 129
},
script: {
type: 'script',
content: '\n' +
"import Hello from '../../components/Hello/Hello';\n" +
'\n' +
'export default {\n' +
' data() {\n' +
' return {};\n' +
' },\n' +
' components: {\n' +
' Hello\n' +
' },\n' +
' methods:{\n' +
' navigateToLogin(){\n' +
' \n' +
' }\n' +
' }\n' +
'};\n',
start: 247,
attrs: {},
end: 467
},
styles: [
{
type: 'style',
content: '\n' +
'.home-wrap {\n' +
' width: 100vw;\n' +
' height: 100vh;\n' +
' display: flex;\n' +
' justify-content: center;\n' +
' align-items: center;\n' +
' flex-direction: column;\n' +
'}\n' +
'.home-text {\n' +
' font-size: 24px;\n' +
' line-height: 1.3;\n' +
' color: #6a8bad;\n' +
' text-align: center;\n' +
'}\n',
start: 485,
attrs: {},
end: 741
}
],
customBlocks: [
{
type: 'config',
content: "\n{\n config: {\n navigationBarTitleText: 'Mars'\n }\n}\n",
start: 164,
attrs: [Object],
end: 228
}
]
}- 然后调用parseConfig将配置内容通过new Function转换成对象形式
- 最终将模板内容传递给wrapFiles,在wrapFiles中通过new File方式将script、template、styles、config模板内容进行包装,然后返回。
我们看一下File的定义:
//src/compiler/sfc/File.js
const Vinyl = require('vinyl');
const fs = require('fs-extra');
Vinyl.prototype.writeFileSync = function () {
if (!this.contents || !this.path) {
throw new Error('Vinyl.prototype.writeFileSync() requires path and contents to write');
}
fs.outputFileSync(this.path, this.contents.toString());
};
Vinyl.prototype.appendContent = function (str) {
const content = this.contents ? this.contents.toString() : '';
this.contents = Buffer.from(content + str);
};
module.exports = Vinyl;需要说明的是这里的 File 不是 Node.js FileSystem 的文件对象,是 Gulp 自创的一种用来描述一个虚拟文件的类 Vinyl,其中主要包括文件的内容和文件的路径两大信息。Vinyl-fs,它主要的工作是接受 glob 模式的参数,然后读取匹配的文件,然后利用 Vinyl 制作一个 Transform Stream,称为 Vinyl Stream 对象,并返回。在 Gulp 中的 API gulp.src、gulp.watch、gulp.dest 都返回一个 Vinyl Stream 实例对象。Vinyl Stream 实例之间可以通过管道 vinyl1.pipe(vinyl2) 的形式来互相传输数据。
编译 SFC 文件
上面通过sfcCompiler解析成script,template,styles,config四段式然后交给了sfcCompiler进行编译。sfcCompiler 是 ./compiler/sfc/compiler 中的 compile 方法,具体如下:
const renderFunctionName = '__renderFunction';
const {getFileCompilers} = require('../file/base');
exports.compile = async function compile(file, options) {
const {template, script, styles, config: configFile} = file;
const blockConfig = configFile.$options.config;
const mpConfig = blockConfig && blockConfig.config;
const marsConfig = options._config;
// const isComponent = mpConfig && mpConfig.component === true;
const {compilers, isApp, fPath, target, coreRelativePath, baseName} = options;
const {
templateCompiler,
scriptCompiler,
scriptPostCompiler,
styleCompiler,
configCompiler
} = getFileCompilers(compilers, options);
let {components, config, computedKeys, moduleType} = await scriptCompiler(script, {
isApp,
mpConfig,
coreRelativePath,
target,
renderStr: !isApp ? renderFunctionName : null,
dest: marsConfig.dest
});
// use configFile.$options.config first
config = mpConfig ? mpConfig : config;
// prefer appConfig in marsConfig
if (isApp) {
const appConfig = marsConfig.appConfig && marsConfig.appConfig.config;
config = appConfig || config;
}
// app.vue has no template
if (!isApp) {
const {render, componentsInUsed} = await templateCompiler(template, {
components,
computedKeys,
target
});
await scriptPostCompiler(script, {
componentsInUsed
});
script.appendContent(
`;\nfunction ${renderFunctionName}() {return ${render + '.render.bind(this)()'};\n}`
);
template.writeFileSync();
}
if (config.component === true) {
script.path = fPath + '.vue.js';
script.writeFileSync();
script.path = fPath + '.js';
const emsImport = `import comp from './${baseName}.vue';\n`
+ `import {createComponent} from '${coreRelativePath}';\n`
+ 'Component(createComponent(comp));\n';
const cmdRequire = `const comp = require('./${baseName}.vue');\n`
+ `const {createComponent} = require('${coreRelativePath}');\n`
+ 'Component(createComponent(comp));\n';
script.contents = Buffer.from(moduleType === 'esm' ? emsImport : cmdRequire);
script.writeFileSync();
}
else {
script.writeFileSync();
}
return Promise.all([
configCompiler(configFile, {components, config}).then(_ => {
configFile.writeFileSync();
}),
styleCompiler(styles, options).then(_ => {
styles.writeFileSync();
})
]);
};在compiler方法中,先获取template, script, styles, config内容,然后通过getFileCompilers获取编译器
function getFileCompiler(compile, config) {
const {preprocessors = {}, postprocessors = {}} = config;
compile = compile || defaultCompile;
return async function fileCompiler(file, options) {
const fileOptions = file.$options;
const lang = file.lang || file.type;
let source = getFileSource(file);
// preprocessors
source = await process(source, getExtProcessors(preprocessors, lang), file);
// compile
options.path = file.path;
options.file = file;
const result = await compile(source, options, fileOptions);
// postprocessors
let {code, ...rest} = result;
code = await process(code, getExtProcessors(postprocessors, lang), file);
// overwrite file contents
file.contents = typeof code === 'string'
? Buffer.from(code || '')
: code;
return rest;
};
}
function getFileCompilers(compilers = {}, options) {
const buildConfig = options._config || {};
let ret = {};
Object.keys(compilers).forEach(key => {
const compiler = compilers[key];
ret[key] = getFileCompiler(compiler, buildConfig);
});
return ret;
}可以看出templateCompiler,scriptCompiler,scriptPostCompiler,styleCompiler,configCompiler是基于gulp-mars-wxml.js 中的 compilers封装一层。
最后依次执行这几个编译器完成编译任务。我们接下来再看看这几个编译器做了哪些内容。
template 编译器
我们看一下gulp-mars-wxml.js中定义的templateCompiler:
const {
getCompiler,
generate,
mark
} = require('./compiler/template/index');
const {transform} = require('./wx/transform/index');
const templateCompiler = getCompiler(mark, transform, generate, 'wx');我们来看下getCompiler的定义:
//src/compiler/template/index
exports.getCompiler = function getCompiler(marker, transformer, generater, target) {
return function compiler(source, options) {
let {ast, render, componentsInUsed} = marker(source, options);
let {ast: myAst} = transformer(ast, options);
options = Object.assign(options, {
target
});
let code = generater(myAst, options);
return {render, code, componentsInUsed};
};
};getCompiler的参数主要有以下几项:
- marker:标记器,其实就是 parser,返回值为:ast(template AST 对象), render(JS 渲染函数), errors(错误信息), componentsInUsed(组件依赖);
- transformer:转换器
- generater:生成器
- target:目标平台
下面我们以一个实际的例子为例加以说明:
Vue template源码如下:
<view class="home-wrap">
<view class="home-text">Vue 驱动的多端开发框架</view>
<Hello></Hello>
</view>options:
{
components: { hello: '../../components/Hello/Hello.vue' },
computedKeys: [],
target: 'wx',
path: '**\\dist-wx\\pages\\home\\index.wxml',
}经过 marker 转换后,生成的ast如下:
{
type: 1,
tag: 'view',
attrsList: [],
attrsMap: { class: 'home-wrap' },
parent: undefined,
children: [
{
type: 1,
tag: 'view',
attrsList: [],
attrsMap: [Object],
parent: [Circular *1],
children: [Array],
ns: 'svg',
plain: false,
staticClass: '"home-text"',
isComp: undefined,
static: false,
staticRoot: false,
pre: undefined
},
{
type: 1,
tag: 'hello',
attrsList: [Array],
attrsMap: [Object],
parent: [Circular *1],
children: [],
ns: 'svg',
plain: false,
isComp: '../../components/Hello/Hello.vue',
hasBindings: true,
attrs: [Array],
static: false,
staticRoot: false,
pre: undefined
}
],
ns: 'svg',
plain: false,
staticClass: '"home-wrap"',
isComp: undefined,
static: false,
staticRoot: false
}render渲染函数如下:
({
render: function () {
var _vm = this;
var _h = _vm.$createElement;
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h;
return [, [, , [[_vm._pp({ 'compId': (_vm.compId ? _vm.compId : '$root') + ',0' })]]]]
}, staticRenderFns: []
})componentsInUsed组件依赖如下
{
hello: {
using: true,
declaration: '../../components/Hello/Hello.vue'
}
}经过 transformer 和 generater 后,最终转换生成后的模版为:
<view class="home-wrap">
<view class="home-text">Vue 驱动的多端开发框架</view>
<hello compId="{{ (compId ? compId : '$root') + ',0' }}"></hello>
</view>其中marker的源码如下:
//src/compiler/template/mark-component
module.exports = function mark(source, options) {
const {
components = {}
} = options;
let componentsInUsed = {};
Object.keys(components).forEach(name => {
if (!componentsInUsed[name]) {
componentsInUsed[name] = {
using: false,
declaration: components[name]
};
}
});
const {
ast,
staticRenderFns,
errors
} = compileTemplate(source, {
preserveWhitespace: false,
modules: [
{
transformNode: getMarkNode(options, componentsInUsed),
postTransformNode: getPostTrans(options)
}
]
});
const render = generate(ast, {
processFilterData: getGenData(),
isComplexExp,
isFilter,
isInFor,
getIterators
});
updateComponents(components, componentsInUsed);
let code = `({ render: function() {${render.render}}, staticRenderFns: [\
${staticRenderFns.map(fn => `function() { ${fn} },)}`)}\
] })`;
code = transpile(code);
return {ast, render: code, errors, componentsInUsed};
};在mark这段逻辑中,source是template模版,options中的components字段包含当前template依赖的组件信息。例如:
source源码:
<view class="home-wrap">
<view class="home-text">Vue 驱动的多端开发框架</view>
<Hello></Hello>
</view>传递过来的options内容:
{
components: { hello: '../../components/Hello/Hello.vue' },
computedKeys: [],
target: 'wx',
path: 'C:\\Users\\18307\\Desktop\\Mars\\packages\\demo\\dist-wx\\pages\\home\\index.wxml',
}首先遍历components,将组件存放在componentsInUsed中,然后调用vue-template-compiler的compile方法去编译,options参数传递了两个, preserveWhitespace是否保留空白,modules可以挂钩编译过程来支持自定义模板功能。
通过编译接口 transformNode 标记使用的组件,没有使用的组件会通过 updateComponents 被移除。在 postTransformNode 中移除了 template-platform 标签 target 不是当前环境变量的组件,这是 template 逻辑的条件编译。
我们看一下transformNode对应的函数getMarkNode的内容:
function getMarkNode(options, componentsInUsed = {}) {
let {components, target} = options;
let compIdCounter = 0;
return function markNode(el, options) {
// swan doesn't support PascalCase tag name
el.tag = hyphenate(el.tag);
const tag = el.tag;
const isComp = components && components[tag];
el.isComp = isComp;
if (isComp && checkCurrentEnvComponent(el, target || process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET)) {
componentsInUsed[tag].using = true;
}
if (el.attrsMap['v-for'] && !el.iterator1) {
el.iterator1 = 'index';
}
if (isComp) {
// TODO:如果用户自己设置了 comId,报 warning
let value;
if (isInFor(el)) {
const iterators = getIterators(el);
const iteratorsIdExpr = iterators.join(' + \'_\' + ');
// value = '(compId ? compId : \'$root\') + ' + '\',' + compIdCounter + '-\' + ' + iterators.join(` + '_' + `);
value = `(compId ? compId : '$root') + ',${compIdCounter}-' + ${iteratorsIdExpr}`;
}
else {
// value = '(compId ? compId : \'$root\') + ' + '\',' + compIdCounter + '\'';
value = `(compId ? compId : '$root') + ',${compIdCounter}'`;
}
el.attrsList.push({
name: ':compId',
value
});
el.attrsMap[':compId'] = value;
compIdCounter++;
}
['v-show', 'v-model'].forEach(dir => {
if (el.attrsMap[dir]) {
const value = el.attrsMap[dir];
el.attrsList.push({
name: `:${dir}`,
value
});
el.attrsMap[`:${dir}`] = value;
}
});
// plain el will skip genData
// mark el with ComplexExp not plain to make filters data generated
if (el.attrsList.length === 0
&& (isComplexExp(el.for) || isComplexExp(el.if) || isComplexExp(el.elseif))
) {
el.plain = false;
}
};
}首先检查el的tag是否在components对象中,并且判断el是否是一个组件。如果是组件,则将el的isComp属性设置为true。
接着,如果el是一个组件,并且在componentsInUsed对象中,则将该组件的using属性设置为true。
然后,如果el有v-for属性,并且没有iterator1属性,则将iterator1属性设置为index。如果el是一个组件,则根据不同的情况设置compId属性。
最后,如果el有v-show或v-model属性,则将这些属性的名称前面加上冒号,并将它们添加到el的attrsList属性中。如果el没有任何属性,并且el的for、if或elseif属性是复杂表达式,则将el的plain属性设置为false.
最终调用vue-template-es2015-compiler进行代码转换。
我们接下来再看transformer的内容
//src/wx/transform/transform.js
function transform(node, options) {
const {
children,
ifConditions,
attrsMap,
tag
} = node;
// const isComp = options && options.components && options.components[tag];
// node.isComp = isComp;
// const ast = Object.assign({}, node);
node.attrsMap = attrsFormat(node, attrsMap);
node = modifyBind(node, val => {
// quick test
if (!/`[\s\S]*`/.test(val)) {
return val;
}
return transformExpression(val, {
plugins: [
['@babel/plugin-transform-template-literals', {
loose: true
}]
]
});
});
// const computedKeys = (options && options.computedKeys) || [];
// if (computedKeys.length > 0) {
// node = modifyBind(node, getComputedModifier(computedKeys));
// }
node = transFilters(node, options);
node.attrsMap = transAttrs(node, options);
if (children) {
node.children = children.map((k, index) => transform(k, options));
}
if (ifConditions) {
ifConditions.forEach((c, i) => {
if (c.block !== node) {
node.ifConditions[i].block = transform(c.block, options);
}
});
}
return node;
}transform是一个递归函数,主要处理marker后的ast树。它主要做了这样几件事情:
- 对节点的属性进行格式化处理,并更新属性映射表。
function attrsFormat(node, attrs = {}) {
const obj = {};
Object.keys(attrs).forEach(key => {
let val = attrs[key];
key = key.replace(/^@/, 'v-on:').replace(/^:/, 'v-bind:');
// 支持函数调用带参数 预处理
if (key.indexOf('v-on:') === 0) {
const [dir, param] = key.split(':');
const [eventName] = param.split('.');
if (val.indexOf('(') > -1) {
const matches = val.match(/([^(]+)\(([^)]+)\)/);
if (matches) {
const handlerName = matches[1].trim();
let args = matches[2];
// mark $event to special string
args = args.split(',').map(a => {
a = a.trim();
return a === '$event' ? '\'_$event_\'' : a;
});
args = `[ ${args.join(',')} ]`;
// modify handlerName and gen args bind
val = handlerName;
obj[`v-bind:data-${eventName}ArgumentsProxy`.toLowerCase()] = args;
}
}
}
obj[key] = val;
});
if (node.isComp) {
// node.attrsMap['v-bind:rootComputed'] = 'compComputed || rootComputed';
node.attrsMap['v-bind:rootUID'] = 'rootUID';
}
return obj;
}该函数会遍历ast的attrsMap,将属性名称中的'@'替换为'v-on:',':'替换为'v-bind:'。如果是v-on函数调用带参数的话会预先处理一下。然后判断ast节点是否有isComp属性,有的话则在attrsMap中添加v-bind:rootUID=rootUID
- 对节点的绑定属性进行处理,包括对绑定属性值进行转换。
@babel/plugin-transform-template-literals:用于将模板字面量转换为普通字符串拼接。
对节点的过滤器进行处理,并更新过滤器映射表。
对节点的属性进行处理,并更新属性映射表。
对节点的子节点进行递归处理,并更新子节点列表。
对节点的条件判断进行处理,并更新条件判断列表。
转换完模版之后,调用generater函数将ast生成模版代码,generater代码如下:
const customTemplate = 'template-mars';
module.exports = function generate(obj, options = {}) {
const {
attrsMap = {},
children,
text,
scopedSlots,
ifConditions
} = obj;
let tag = obj.tag;
if (!tag) {
return text;
}
if (tag === customTemplate && (process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET || options.target) !== attrsMap.target) {
return;
}
else if (tag === customTemplate) {
tag = 'block';
delete attrsMap.target;
}
let child = '';
if (children && children.length > 0) {
child = children.map(v => generate(v, options)).join('');
}
let slots = '';
if (scopedSlots) {
slots = Object.keys(scopedSlots).map(k => generate(scopedSlots[k], options)).join('');
}
let ifConditionsArr = [];
if (ifConditions && ifConditions.length > 0) {
ifConditionsArr = ifConditions.slice(1).map(item => generate(item.block, options));
}
const attrs = Object.keys(attrsMap).map(k => convertAttr(k, attrsMap[k])).join(' ');
const ifText = ifConditionsArr.join('');
let spaceLine = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'dev' ? '\n' : '';
const tags = ['progress', 'switch', 'input', 'slider', 'textarea'];
if (tags.indexOf(tag) > -1) {
return `${spaceLine}<${tag}${attrs ? ' ' + attrs : ''} />${ifText}`;
}
return `${spaceLine}<${tag}${attrs ? ' ' + attrs : ''}>${child || ''}${slots || ''}</${tag}>${ifText}`;
};
function convertAttr(key, val) {
return (val === '' || typeof val === 'undefined') ? key : `${key}="${val.replace(/\"/g, '\\"')}"`;
}首先先从ast节点中获取tag、attrsMap、children、text、scopedSlots和ifConditions,tag属性是一个字符串,表示HTML标签的名称。 attrsMap属性是一个对象,包含了HTML标签的属性和值。children属性是一个数组,包含了子标签的对象。text属性是一个字符串,表示标签的文本内容。scopedSlots属性是一个对象,包含了标签的作用域插槽。ifConditions属性是一个数组,包含了条件判断的对象。
函数首先检查tag属性是否为空。如果为空,则返回text属性的值。然后,函数检查tag属性是否等于customTemplate,并且(process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET或options.target)不等于attrsMap.target。如果是这种情况,则返回空。否则,如果tag属性等于customTemplate,则将tag属性设置为'block',并删除attrsMap.target属性。接下来,函数检查children属性是否为空,并且children数组的长度大于0。如果是这种情况,则使用generate函数递归地生成子标签的HTML标签,并将它们连接起来。
然后,函数检查scopedSlots属性是否为空。如果是这种情况,则使用generate函数递归地生成作用域插槽的HTML标签,并将它们连接起来。 接下来,函数检查ifConditions属性是否为空,并且ifConditions数组的长度大于0。如果是这种情况,则使用generate函数递归地生成条件判断的HTML标签,并将它们连接起来。
最后,函数检查tag属性是否为'progress'、'switch'、'input'、'slider'或'textarea'。如果是这种情况,则返回一个自闭合标签。否则,返回一个开始标签、子标签和作用域插槽的HTML标签,以及条件判断的HTML标签。
在函数中,还有一个convertAttr函数,用于将attrsMap对象中的键值对转换为HTML属性的字符串。
script 编译器
script编译器提供了两个编译能力,分别是compile和postCompile。我们分别看一下这两个的实现。
我们先看一下compile的实现:
//src/compiler/script
async function compile(source, options) {
const {
isApp,
mpConfig,
renderStr,
coreRelativePath,
target,
dest
} = options;
let ret = {};
source = source.replace(
/process\.env\.MARS_ENV/g,
JSON.stringify(target)
).replace(
/process\.env\.NODE_ENV/g,
JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development')
);
const scriptAST = transformSync(source, {
ast: true,
code: false,
plugins: [
transformPlugin({
file: ret,
coreRelativePath,
isApp,
mpConfig,
renderStr,
target
})
]
}).ast;
// let code = scriptRet.code;
const {
config = {},
components = {},
computedKeys = [],
moduleType = 'esm'
} = ret;
const uiModules = getUIModules(components, target);
// 处理完再进行minify,发现minify和定制的插件会有坑
const destPath = path.resolve(dest.path);
const rPath = path.relative(path.dirname(options.path), destPath);
let usedModules = {};
const minifyScriptRet = transformFromAstSync(scriptAST, source, {
plugins: [
[
path.resolve(__dirname, '../file/babel-plugin-relative-import.js'),
{
rPath,
modules: Object.assign({}, modules, uiModules),
usedModules,
compileNPM: process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET === 'wx'
}
],
'minify-guarded-expressions',
'minify-dead-code-elimination'
]
});
const code = minifyScriptRet.code;
const usedModuleKeys = Object.keys(usedModules);
for (let i = 0; i < usedModuleKeys.length; i++) {
const key = usedModuleKeys[i];
const info = usedModules[key];
const {modName, path} = info;
if (!uiModules[modName]) {
await compileModules.compile(key, path, destPath);
}
}
resolveComponentsPath(components, usedModules);
await compileModules.compileUIModules(uiModules, destPath);
return {code, config, components, computedKeys, moduleType};
}函数首先将process.env.MARS_ENV替换为目标环境(target),这部分的作用是提供JS 逻辑适配的能力,process.env.NODE_ENV替换为当前环境(development或production)。
然后调用transformSync转换ast,并传递了ast:true和code:false,Babel的默认设置是生成一个字符串和一个源映射,但是我们这里需要获取AST,这方面的主要用例是一个多个变换过程的链,在一些对Babel进行多次调用的情况下,所以我们需要使用code:false禁用代码生成并使用ast:true直接获取ast。然后传递了transformPlugin插件。
我们看一下transformPlugin插件的代码:
//src/compiler/script/babel-plugin-script.js
const {hyphenate} = require('../../helper/util');
function getPlainObjectNodeValue(node, path, t) {
let result;
if (t.isObjectExpression(node)) {
result = {};
let props = node.properties || [];
for (let i = 0, len = props.length; i < len; i++) {
let subNode = props[i];
let keyNode = subNode.key;
let key;
if (t.isLiteral(keyNode)) {
key = keyNode.value;
}
else if (t.isIdentifier(keyNode)) {
key = keyNode.name;
}
if (!key) {
continue;
}
result[key] = getPlainObjectNodeValue(subNode.value, path, t);
}
}
else if (t.isArrayExpression(node)) {
result = [];
node.elements.forEach(item => {
result.push(getPlainObjectNodeValue(item, path, t));
});
}
else if (t.isLiteral(node)) {
result = node.value;
}
else {
throw path.buildCodeFrameError('config field should not contain variables');
}
return result;
}
const getPropertyVisitor = (t, options) => {
return {
ObjectProperty(path, state) {
const propName = path.node.key.name;
// 如果没有定义区块级的 config
if (propName === 'config' && !options.mpConfig) {
const configValue = getPlainObjectNodeValue(path.node.value, path, t) || {};
if (options.isApp) {
if (configValue.pages) {
configValue.pages = configValue.pages.map(item => item.replace(/\.(swan|mp)$/, ''));
}
if (configValue.subPackages && configValue.subPackages.length > 0) {
configValue.subPackages = configValue.subPackages.map(item => {
if (!item.pages || item.pages.length === 0) {
return item;
}
const pageArr = [];
item.pages.forEach(route => pageArr.push(route.replace(/\.(swan|mp)$/, '')));
item.pages = pageArr;
return item;
});
}
if (configValue.tabBar && configValue.tabBar.list) {
configValue.tabBar.list = configValue.tabBar.list.map(item => {
item.pagePath = item.pagePath.replace(/\.(swan|mp)$/, '');
return item;
});
}
}
options.file && (options.file.config = configValue);
path.remove();
}
if (propName === 'components') {
if (t.isObjectExpression(path.node.value)) {
let components = {};
path.node.value.properties.forEach(p => {
if (t.isIdentifier(p.value)) {
const name = p.value.name;
const binding = path.scope.bindings[name];
if (!binding) {
throw path.buildCodeFrameError(`cannot find binding for component "${p.value.name}"`);
}
let keyName = t.isLiteral(p.key) ? p.key.value : p.key.name;
keyName = hyphenate(keyName);
const bindPath = binding.path;
const bindParentNode = bindPath.parent;
const bindNode = bindPath.node;
if (t.isImportDeclaration(bindParentNode)) {
const bindVaule = bindParentNode.source.value.replace(/\.vue$/, '') + '.vue';
components[keyName] = bindVaule;
bindParentNode.source = t.stringLiteral(bindVaule);
}
else if (t.isVariableDeclaration(bindParentNode)
&& t.isVariableDeclarator(bindNode)
&& t.isCallExpression(bindNode.init)
&& t.isIdentifier(bindNode.init.callee)
&& bindNode.init.callee.name === 'require'
&& t.isStringLiteral(bindNode.init.arguments[0])
) {
const bindVaule = bindNode.init.arguments[0].value.replace(/\.vue$/, '') + '.vue';
components[keyName] = bindVaule;
bindNode.init.arguments[0] = t.stringLiteral(bindVaule);
}
else {
throw path.buildCodeFrameError('binding should in stitic require or import '
+ `for component "${p.value.name}"`);
}
}
});
options.file && (options.file.components = components);
}
}
// computedKeys方案已被废弃,不需要处理computed属性
// if (propName === 'computed') {
// if (t.isObjectExpression(path.node.value)) {
// const keys = path.node.value.properties.map(p => p.key.name);
// options.file && (options.file.computedKeys = keys);
// }
// }
// skip child traverse
path.skip();
}
};
};
function transfromSFCExport(t, declarationPath, options) {
if (!t.isObjectExpression(declarationPath)) {
throw declarationPath.buildCodeFrameError('should export plain object or Vue.extend() in SFC');
}
declarationPath.traverse(getPropertyVisitor(t, options));
if (options.renderStr) {
declarationPath.node.properties.push(t.objectProperty(
t.identifier('render'),
t.identifier(options.renderStr)
));
}
}
function capitalize(s) {
if (typeof s !== 'string') {
return '';
}
return s.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + s.slice(1);
}
module.exports = function getVisitor(options = {}) {
return ({types: t}) => {
let exportPath;
let declarationPath;
const {
file,
isApp,
mpConfig,
target
} = options;
return {
visitor: {
ExportDefaultDeclaration(path, state) {
declarationPath = path.get('declaration');
// 只取 Vue.extend() 的参数部分
if (t.isCallExpression(declarationPath)) {
const objectExpression = declarationPath.get('arguments')[0];
declarationPath.replaceWith(objectExpression);
}
transfromSFCExport(t, declarationPath, options);
exportPath = path;
file.moduleType = 'esm';
},
AssignmentExpression(path, state) {
let leftNode = path.node.left;
if (t.isMemberExpression(leftNode)) {
let objName = leftNode.object.name;
let propName = leftNode.property.name;
if (objName === 'module' && propName === 'exports') {
declarationPath = path.get('right');
transfromSFCExport(t, declarationPath, options);
exportPath = path;
file.moduleType = 'cmd';
// skip child traverse
path.skip();
}
}
},
Program: {
exit(path) {
if (!exportPath || !declarationPath) {
throw path.buildCodeFrameError('should has export in SFC');
}
const isComponent = mpConfig ? mpConfig.component : (file.config && file.config.component);
const mpType = isApp
? 'app'
: isComponent ? 'component' : 'page';
if (mpType === 'app' || mpType === 'page') {
let fnName = capitalize(mpType);
const createFnName = `create${fnName}`;
// use Component create Page for right comp sequence
if (target === 'wx' && mpType === 'page') {
fnName = 'Component';
}
exportPath.replaceWith(t.callExpression(
t.identifier(fnName),
[t.callExpression(
t.identifier(createFnName),
[declarationPath.node]
)]
));
path.node.body.unshift(
t.importDeclaration([
t.importSpecifier(
t.identifier(createFnName),
t.identifier(createFnName)
)
],
t.stringLiteral(options.coreRelativePath)
)
);
}
if (mpType === 'component') {
declarationPath.replaceWith(
t.callExpression(
t.identifier('vueCompCreator'),
[declarationPath.node]
)
);
path.node.body.unshift(
t.importDeclaration(
[
// t.importSpecifier(
// t.identifier('createComponent'),
// t.identifier('createComponent')
// ),
t.importSpecifier(
t.identifier('vueCompCreator'),
t.identifier('vueCompCreator')
)
],
t.stringLiteral(options.coreRelativePath)
)
);
}
}
}
}
};
};
};然后再调用transformFromAstSync将我们刚刚修改的ast转编回我们的代码,并传入相关插件:
- minify-guarded-expressions:用于通配符类型的条件表达式的优化。它可以帮助开发者减少冗长的条件判断语句,提高代码的可读性和性能。
- minify-dead-code-elimination:用于在编译时删除未使用的代码。它可以帮助减少 JavaScript 文件的大小,从而加快网页的加载速度。
还有我们自定义的插件babel-plugin-relative-import,
module.exports = function ({types: t}) {
return {
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration(babelPath, state) {
const {rPath, modules, usedModules = {}, compileNPM = false} = state.opts;
const name = babelPath.node.source.value;
const modName = getModuleName(name);
if (modName && (compileNPM || modules[modName])) {
let modulePath = getModulePath(name, modules).replace(/\.js$/, '');
let relativePath = path.join(rPath, modulePath);
if (relativePath[0] !== '.') {
relativePath = './' + relativePath;
}
const resolvedPath = name.replace(modName, relativePath);
usedModules[name] = {
modName,
path: modulePath,
resolvedPath
};
babelPath.node.source.value = resolvedPath;
}
},
CallExpression(nodePath, state) {
const node = nodePath.node;
const callee = node.callee;
const arg = node.arguments[0];
if (callee.type !== 'Identifier' || callee.name !== 'require' || !arg || arg.type !== 'StringLiteral') {
return;
}
const {rPath, modules, usedModules = {}, compileNPM = false} = state.opts;
const name = arg.value;
const modName = getModuleName(name);
if (modName && (compileNPM || modules[modName])) {
let modulePath = getModulePath(name, modules).replace(/\.js$/, '');
let relativePath = path.join(rPath, modulePath);
if (relativePath[0] !== '.') {
relativePath = './' + relativePath;
}
const resolvedPath = name.replace(modName, relativePath);
usedModules[name] = {
modName,
path: modulePath,
resolvedPath
};
nodePath.replaceWith(
t.callExpression(callee, [t.stringLiteral(resolvedPath)])
);
// babelPath.node.source.value = resolvedPath;
}
}
}
};
};最后,返回编译结果。
postCompile代码如下:
//src/compiler/script
async function postCompile(source, options) {
const {componentsInUsed} = options;
const scriptRet = transformSync(source, {
plugins: [
postTransformPlugin({
componentsInUsed
})
]
});
return {code: scriptRet.code};
}postCompile函数接收两个参数:source和options,source是一个字符串,表示需要处理的代码。options是一个对象,其中包含了componentsInUsed属性。函数返回一个对象,对象中包含了一个属性code,其值为处理后的代码。
在函数内部,使用了一个名为transformSync的函数,配置选项中包含了一个名为plugins的属性,这个属性是一个数组,数组中包含了一个名为postTransformPlugin的函数。
我们看一下transformSync的内容:
//src/helper/babel.js
const {transformSync, transformFromAstSync} = require('@babel/core');
const DEFAULT_OPTIONS = {
configFile: false,
babelrc: false
};
exports.transformSync = function (code, opts = {}) {
return transformSync(code, Object.assign(opts, DEFAULT_OPTIONS));
};我们可以看到transformSync基于@babel/core库提供的transformSync封装,并默认提供了一些配置选项。
所以我们看到transformSync的options配置中配置了plugins插件数组。
而postTransformPlugin就是我们定义的插件,里面传递了componentsInUsed。我们具体看一下其内容。
//src/compiler/script/babel-plugin-script-post.js
const {hyphenate} = require('../../helper/util');
module.exports = function getVisitor(options = {}) {
return ({types: t}) => {
const {
componentsInUsed
} = options;
return {
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration(path, state) {
const sourcePath = path.node.source;
if (sourcePath) {
Object.keys(componentsInUsed).forEach(comp => {
componentsInUsed[comp].declaration === sourcePath.value
&& !componentsInUsed[comp].using
&& path.remove();
});
}
},
ObjectProperty(path, state) {
if (path.node.key.name !== 'components') {
return;
}
path.traverse({
ObjectProperty(path, state) {
let componentName = path.node.key.type === 'Identifier'
? path.node.key.name
: path.node.key.type === 'StringLiteral'
? path.node.key.value
: null;
componentName = hyphenate(componentName);
if (componentName && !componentsInUsed[componentName].using) {
path.remove();
}
}
});
}
}
};
};
};该函数接收一个参数options,options是一个对象,包含componentsInUsed属性。componentsInUsed是一个对象,其中包含多个组件的声明和使用情况。
这个函数返回一个对象,该对象包含一个visitor属性,visitor是一个对象,包含两个函数:ImportDeclaration和ObjectProperty。
ImportDeclaration函数用于处理导入声明,它会遍历componentsInUsed对象,找到sourcePath.value与componentsInUsed对象中的declaration属性相等,并且componentsInUsed对象中的using属性为false的组件,然后将该导入声明删除。
ObjectProperty函数用于处理对象属性,它会遍历componentsInUsed对象,找到key.name不等于'components'的属性,并且将其删除。
在ObjectProperty函数中,它会再次遍历componentsInUsed对象,找到key.name等于'components'的属性,并且将其删除。
hyphenate函数用于将字符串中的大写字母转换为连字符格式,例如将'HelloWorld'转换为'hello-world'。
最后,这个函数返回一个对象,该对象包含一个visitor属性,visitor是一个对象,包含两个函数:ImportDeclaration和ObjectProperty。
config编译器
config编译器比较简单,我们看一下代码:
exports.compile = function compile(source, options) {
const {config, components = {}} = options;
Object.keys(components).forEach(k => {
components[k] = components[k].replace(/\.vue$/, '');
});
config.usingComponents = Object.assign(components, config.usingComponents || {});
return {
code: JSON.stringify(config)
};
};首先从options中获取了config和components两个对象。接着,我们遍历components对象,并将其中的每个键值对应的值中的.vue后缀去掉。
然后,我们将components对象赋值给config.usingComponents属性,如果config.usingComponents已经存在,则将components对象与config.usingComponents对象进行合并。
最后,我们将config对象转换为JSON字符串,并将其作为返回结果。该函数的作用就是将vue组件中config配置转换为小程序的json配置。
style编译器
style编译器主要使用postcss工具来实现的。我们看一下代码:
//src/compiler/style/style.js
const postcss = require('postcss');
const {changeExt} = require('../../helper/path');
const px2units = require('postcss-px2units');
const importPlugin = postcss.plugin('postcss-import-plugin', function (opts = {}) {
let {cssExt} = opts;
cssExt = '.' + cssExt;
return function (root, result) {
root.walkAtRules('import', rule => {
try {
let params = JSON.parse(rule.params);
params = changeExt(params, cssExt);
rule.replaceWith(postcss.atRule({name: 'import', params: JSON.stringify(params)}));
} catch (e) {
throw new Error('[postcss] parse import rule fail: ' + e.message);
}
});
};
});
exports.compile = function compile(source, options = {}) {
/* eslint-disable fecs-camelcase */
const {fileSuffix, _config: buildConfig} = options;
/* eslint-enable fecs-camelcase */
const {designWidth, modules} = buildConfig;
const px2unitsOptions = modules.postcss.px2units;
const cssExt = fileSuffix.css;
let postcssPlugins = [
importPlugin({cssExt})
];
if (px2unitsOptions !== false && designWidth) {
postcssPlugins.push(px2units(px2unitsOptions || {}));
}
const processor = postcss(postcssPlugins);
options.from = undefined;
return processor.process(source, options).then(res => {
return {
code: res.css
};
}).catch(e => {
throw new Error(e);
});
};这段代码是一个PostCSS插件,用于处理CSS文件中的导入语句和像素单位转换。
首先,我们需要了解一下PostCSS是什么:PostCSS是一个用于处理CSS的工具集,可以用来编写CSS预处理器(如Sass、Less)和后处理器(如Autoprefixer、CSSNano)。
在这段代码中,我们首先引入了PostCSS模块,并定义了一个名为postcss-import-plugin的插件。这个插件的作用是将CSS文件中的导入语句处理成PostCSS可以理解的格式。
然后,我们定义了一个函数compile,这个函数的作用是将输入的CSS代码进行编译。在这个函数中,我们首先定义了一些变量,如designWidth、modules、px2unitsOptions和cssExt。
接着,我们定义了一个postcssPlugins数组,用于存储我们要应用到CSS代码上的PostCSS插件。在这个数组中,我们首先添加了postcss-import-plugin插件,然后根据buildConfig中的设置,判断是否需要添加px2units插件。
最后,我们创建了一个PostCSS处理器processor,并使用它来处理输入的CSS代码。处理结果会返回一个包含编译后的CSS代码的对象。
这段代码的主要目的是将输入的CSS代码进行编译,并将处理结果返回。
Assets编译任务
Assets编译主要调用了getTaskCompileAssets函数,我们看一下代码:
function getTaskCompileAssets(config, options) {
const isBinary = require('gulp-is-binary');
const { source } = config;
const { target } = options;
const dest = config.dest.path;
let { assets = [], h5Template } = source;
// if (target === 'h5' && h5Template) {
// assets = assets.concat([h5Template]);
// }
const compileFile = require('../compiler/file/compiler').gulpPlugin;
options.fileSuffix = FILE_SUFFIX[target];
options._config = config;
const logger = config.verbose ? log.info : log.write;
return () => {
if (!assets || (Array.isArray(assets) && assets.length === 0)) {
return Promise.resolve('[warning] empty assets globs');
}
return gulp.src(assets, { allowEmpty: true })
.pipe(changed(dest))
.pipe(intercept(file => {
file.isBuffer() && logger('[compile:assets]:', getPathToCWD(file.path));
return file;
}))
.pipe(isBinary())
.pipe(compileFile(options))
.pipe(gulp.dest(dest));
};
}首先,我们导入了gulp-is-binary,从输入的config对象中获取了源文件路径和目标文件路径。
接着,我们从源文件对象中获取了资源文件的列表。然后引入了compileFile函数来编译文件。
最后我们返回一个函数,在这个函数中,我们首先检查资源文件列表是否为空。
然后使用gulp库来读取资源文件,在读取资源文件的过程中,我们使用了gulp-changed插件来检查文件是否已经被修改过,如果已经被修改过,我们不再进行编译。接着,我们使用了gulp-intercept插件来拦截读取的文件,并进行一些额外的处理,如打印日志等。
然后,我们使用gulp-is-binary插件来判断文件是否为二进制文件,最后调用自定义的compileFile函数去编译资源。
我们接下来看看compileFile函数的代码:
//src/compiler/file/compiler.js
exports.gulpPlugin = function (options) {
const stream = through.obj(function (file, enc, cb) {
if (file.isStream()) {
this.emit('error', new PluginError(PLUGIN_NAME, 'Streams are not supported!'));
return cb();
}
if (file.isBuffer()) {
compile(file, options)
.then(_ => cb(null, file))
.catch(err => {
log.error('[COMPILE ERROR]:', err);
cb(null, file);
});
return;
}
// for other file type
cb(null, file);
});
return stream;
};这个插件使用了through.obj函数来创建一个流来接收文件对象,并且处理这些文件。
然后判断文件的类型,如果文件是一个流,那么它会抛出一个错误并结束流的处理。如果文件是一个缓冲区,那么它会调用compile函数来编译这个文件。如果编译过程中出现错误,它会打印出错误信息并继续处理下一个文件。
最后,如果文件不是流也不是缓冲区,那么它会直接将文件传递给下一个处理函数。
然后我们再看看compile函数做了什么。
//src/compiler/file/compiler.js
async function compile(file, options) {
const {fileSuffix, target} = options;
const buildConfig = options._config || {};
file.lang = path.extname(file.path).substr(1);
if (isCSS(file.path)) {
file.type = 'css';
file.path = changeExt(file.path, fileSuffix.css);
const cssCompiler = getFileCompiler(compileStyle, buildConfig);
await cssCompiler(file, options);
}
else if (isJS(file.path)) {
file.type = 'js';
// TODO: H5 支持 ts 文件编译
if (target !== 'h5') {
file.path = changeExt(file.path, fileSuffix.js);
}
const jsCompiler = getFileCompiler(compileJS, buildConfig);
await jsCompiler(file, options);
}
else {
// for other files, use default compiler
const compiler = getFileCompiler(null, buildConfig);
await compiler(file, options);
}
return file;
}首先获取fileSuffix和target属性,将file.path的扩展名提取出来。
然后,判断file.path是否是CSS文件,如果是,则将file.type设置为'css',将file.path的扩展名改为fileSuffix.css,然后调用CSS编译器compileStyle进行编译。
如果file.path是JS文件,且target不等于h5,则将file.path的扩展名改为fileSuffix.js,最终调用compileJS去编译JS。
如果file.path既不是CSS文件也不是JS文件,其他文件,则调用getFileCompiler函数进行编译。
最后,返回file。
JS编译
我们来看看compileJS编译器做了啥。
/**
* 编译 JS
*
* @param {string} content 文件内容
* @param {mars.options} options opt
* @return {babel.BabelFileResult}
*/
async function compileJS(content, options) {
const {
target,
file
} = options;
const buildConfig = options._config;
content = content.replace(
/process\.env\.MARS_ENV/g,
JSON.stringify(process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET || target)
).replace(
/process\.env\.NODE_ENV/g,
JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development')
);
const destPath = path.resolve(buildConfig.dest.path);
const rPath = path.relative(path.dirname(file.path), file.base);
const modules = target === 'h5' ? compileModules.H5Modules : compileModules.modules;
let usedModules = {};
let res = transformSync(content, {
plugins: [
[
path.resolve(__dirname, './babel-plugin-relative-import.js'),
{
rPath,
modules,
usedModules,
compileNPM: process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET === 'wx'
}
],
'minify-guarded-expressions',
'minify-dead-code-elimination'
]
});
const usedModuleKeys = Object.keys(usedModules);
for (let i = 0; i < usedModuleKeys.length; i++) {
const key = usedModuleKeys[i];
const info = usedModules[key];
const {path} = info;
// if (!uiModules[modName]) {
await compileModules.compile(key, path, destPath);
// }
}
return res;
}首先会对 content 进行一些替换操作,将 process.env.MARS_ENV 替换为 process.env.MARS_ENV_TARGET 或 options.target,将 process.env.NODE_ENV 替换为 process.env.NODE_ENV 或 'development'。
然后,通过 Babel 编译器对 content 进行编译,并返回编译结果。
CSS编译
compileStyle主要是调用了SFC编译过程中使用的CSS编译器,这里就不再讲述了。
其他文件编译
默认其他文件编译调用getFileCompiler进行编译,我们看一下:
//src/compiler/file/base.js
function getFileCompiler(compile, config) {
const {preprocessors = {}, postprocessors = {}} = config;
compile = compile || defaultCompile;
return async function fileCompiler(file, options) {
const fileOptions = file.$options;
const lang = file.lang || file.type;
let source = getFileSource(file);
// preprocessors
source = await process(source, getExtProcessors(preprocessors, lang), file);
// compile
options.path = file.path;
options.file = file;
const result = await compile(source, options, fileOptions);
// postprocessors
let {code, ...rest} = result;
code = await process(code, getExtProcessors(postprocessors, lang), file);
// overwrite file contents
file.contents = typeof code === 'string'
? Buffer.from(code || '')
: code;
return rest;
};
}该函数如果不传编译器的情况下默认只是读取文件。
Runtime编译任务
我们先来看一下Runtime编译任务的定义:
function getTaskRuntime(config, options) {
const {dest: buildDest, source} = config;
// let dest = buildDest.path + '/' + buildDest.coreDir;
let framework = JSON.stringify({});
try {
framework = JSON.stringify(config.framework || {});
}
catch (e) {
throw new Error('config.framework must be plain Object');
}
const compileFile = require('../compiler/runtime/compiler').compile;
const logger = config.verbose ? log.info : log.write;
return () => {
logger('[compile:runtime]:', options.target);
return compileFile({
framework,
target: options.target,
dest: buildDest
});
};
}函数内部获取定义好的framework运行时的配置,然后调用runtime编译器去编译运行时代码。我们接下来看看runtime编译器。
runtime编译器
//src/compiler/runtime/compiler
/**
* compile
*
* @param {mars.runtime.runtimeGulpPluginOptions} options options
* @return {Promise}
*/
function compile(options) {
const {target, dest, framework} = options;
const destPath = dest.path;
let entry;
const coreDestDir = path.resolve(process.cwd(), destPath + '/' + dest.coreDir);
if (target === 'wx') {
entry = require.resolve('@marsjs/core/src/wx', {
paths: [process.cwd()]
});
}
else if (target === 'swan') {
entry = require.resolve('@marsjs/core/src/swan', {
paths: [process.cwd()]
});
}
else if (target === 'h5') {
// h5 runtime just copy it
entry = require.resolve('@marsjs/core/src/h5', {
paths: [process.cwd()]
});
const entryDir = path.dirname(entry);
const files = fs.readdirSync(entryDir);
return Promise.all(files.map(file => fs.copy(
path.resolve(entryDir, file),
path.resolve(process.cwd(), destPath, file)
)));
}
else {
return Promise.resolve();
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
webpack({
entry: [entry],
output: {
path: coreDestDir,
filename: 'index.js',
libraryTarget: 'commonjs'
},
devtool: false,
mode: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'production' : 'development',
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env.MARS_CONFIG_FRAMEWORK': framework
})
]
}, (err, stats) => {
if (err) {
log.error(err.stack || err);
if (err.details) {
log.error(err.details);
}
return resolve();
}
const info = stats.toJson();
if (stats.hasErrors()) {
log.error(info.errors);
}
if (stats.hasWarnings()) {
log.warn(info.warnings);
}
resolve();
// Done processing
});
});
// log.info('[compile:runtime]:', getPathToCWD(file.path));
// let source = (file.contents && file.contents.toString()) || '';
// source = source.replace(
// /process\.env\.NODE_ENV/g,
// JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development')
// ).replace(
// /process\.env\.MARS_CONFIG_FRAMEWORK/g,
// options.framework
// );
// const ret = transform(source, {
// plugins: [
// 'minify-guarded-expressions',
// 'minify-dead-code-elimination'
// ]
// });
// file.contents = Buffer.from(ret.code || '');
// return file;
}首先会获取编译目标平台、编译后的目录、和框架类型,然后根据目标平台的不同,获取不同的入口文件(entry)进行编译。
像微信小程序获取@marsjs/core包下的src/wx作为入口文件进行编译。
对于h5平台,会直接将入口文件中的所有文件复制到输出目录。
对于其他平台会使用webpack进行编译,并将编译后的代码输出到运行时指定的目录。
