装饰器模式
介绍
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)允许向一个现有的对象添加新的功能,同时又不改变其结构。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它是作为现有的类的一个包装。动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,装饰器模式相比生成子类更为灵活。
例如,手机上套一个壳可以保护手机,壳上粘一个指环,可以挂在手指上不容易滑落,这就是一种装饰。手机还是那个手机,手机的功能一点都没变,只是在手机的外面装饰了一些其他附加的功能。日常生活中,这样的例子非常多。

ts
function decorate(phone) {
phone.fn3 = function () {
console.log('指环')
}
}
const phone = {
name: 'iphone12',
fn1() {}
fn2() {}
}
const newPhone = decorate(phone)而 ES 语法允许我们这样写(其实就是语法糖),后面会详细讲
ts
// 伪代码,不能运行
@decorate
const phone = { ... }演示
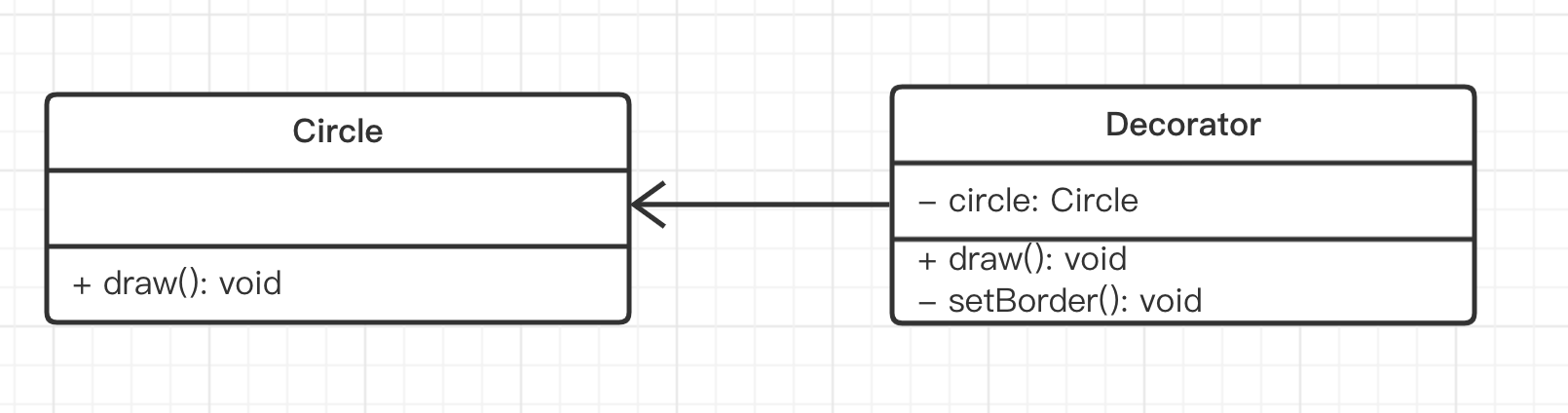
ts
class Circle {
draw() {
console.log('画一个圆')
}
}
class Decorator {
private circle: Circle
constructor(circle: Circle) {
this.circle = circle
}
draw() {
this.circle.draw()
this.setBorder()
}
private setBorder() {
console.log('设置边框颜色')
}
}
const circle = new Circle()
circle.draw()
const decorator = new Decorator(circle)
decorator.draw()是否符合设计原则?
5 大设计原则中,最重要的就是:开放封闭原则,对扩展开放,对修改封闭
- 装饰器和目标分离,解耦
- 装饰器可自行扩展
- 目标也可自行扩展
场景
ES 引入了 Decorator 语法,TS 也支持
PS:在 tsconfig.json 中加 experimentalDecorators: true
装饰 class
ts
// 装饰器
function testable(target: any) {
target.isTestable = true
}
@testable
class Foo {
static isTestable?: boolean
}
console.log(Foo.isTestable) // true可以传入参数
ts
// 装饰器工厂函数
function testable(val: boolean) {
// 装饰器
return function (target: any) {
target.isTestable = val
}
}
@testable(false)
class Foo {
static isTestable?: boolean
}
console.log(Foo.isTestable) // false装饰 class 方法
ts
function readOnly(target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
// console.log('target', target)
// console.log('key', key)
descriptor.writable = false
}
function configurable(val: boolean) {
return function (target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
descriptor.configurable = val
}
}
class Foo {
private _name = '张三'
private _age = 20
@readOnly
getName() {
return this._name
}
@configurable(false)
getAge() {
return this._age
}
}
const f = new Foo()
// f.getName = () => { return 'hello' } // 会报错
console.log(f.getName())
// @ts-ignore
// console.log( Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(f.__proto__, 'getAge') ) // { configurable: false }
console.log(f.getAge)PS:其实 TS 本身有 readOnly 语法,但这里就是一个演示。
react-redux
react-redux 的基本使用如下。文档参考 https://www.redux.org.cn/docs/basics/UsageWithReact.html
js
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
const VisibleTodoList = connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(TodoList)
export default VisibleTodoList如果使用装饰器就是
js
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
// 装饰器
@connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)
export default VisibleTodoList extends React.Component { }Angular 定义组件
ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
// 装饰器,定义 class 为组件
@Component({
selector: 'app-product-alerts',
templateUrl: './product-alerts.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./product-alerts.component.css']
})
export class ProductAlertsComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {}
}AOP
介绍
AOP - Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程
简单来说:业务和系统基础功能分离,用 Decorator 很合适
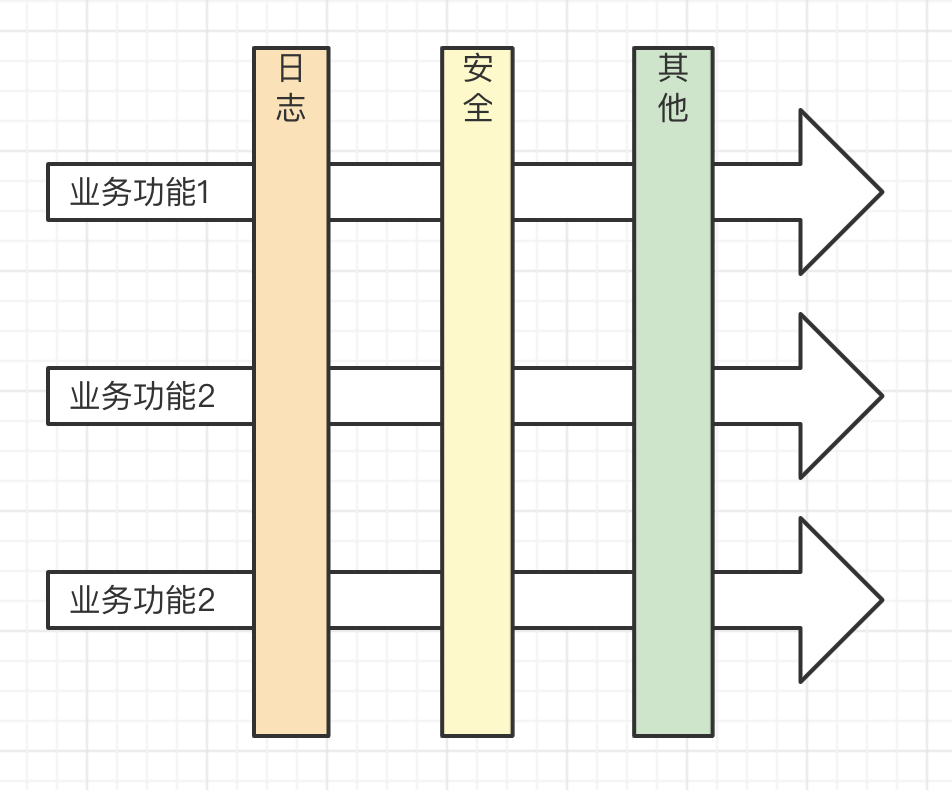
PS:AOP 和 OOP 并不冲突
实现 log
ts
function log(target: any, key: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
const oldValue = descriptor.value // fn1 函数
// 重新定义 fn1 函数
descriptor.value = function () {
console.log(`记录日志...`)
return oldValue.apply(this, arguments)
}
}
class Foo {
@log // 不影响业务功能的代码,只是加了一个 log 的“切面”
fn1() {
console.log('业务功能1')
}
}
const f = new Foo()
f.fn1()