代理模式
介绍
为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。在直接访问对象时带来的问题,比如说:要访问的对象在远程的机器上。在面向对象系统中,有些对象由于某些原因(比如对象创建开销很大,或者某些操作需要安全控制,或者需要进程外的访问),直接访问会给使用者或者系统结构带来很多麻烦,我们可以在访问此对象时加上一个对此对象的访问层。
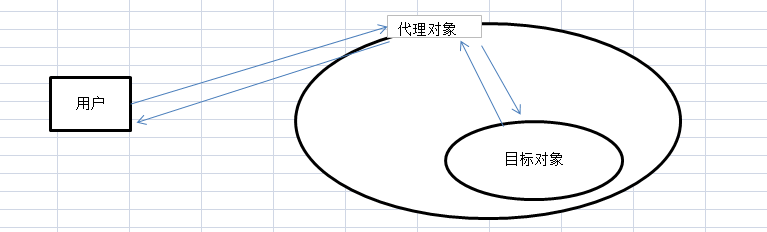
例如,你通过房产中介买房子,中介就是一个代理。你接触到的是中介这个代理,而非真正的房主。
再例如,明星都有经纪人,某活动想请明星演出,需要对接经纪人。艺术家不方便谈钱,但可以和经纪人谈。经纪人就是一个代理。
演示
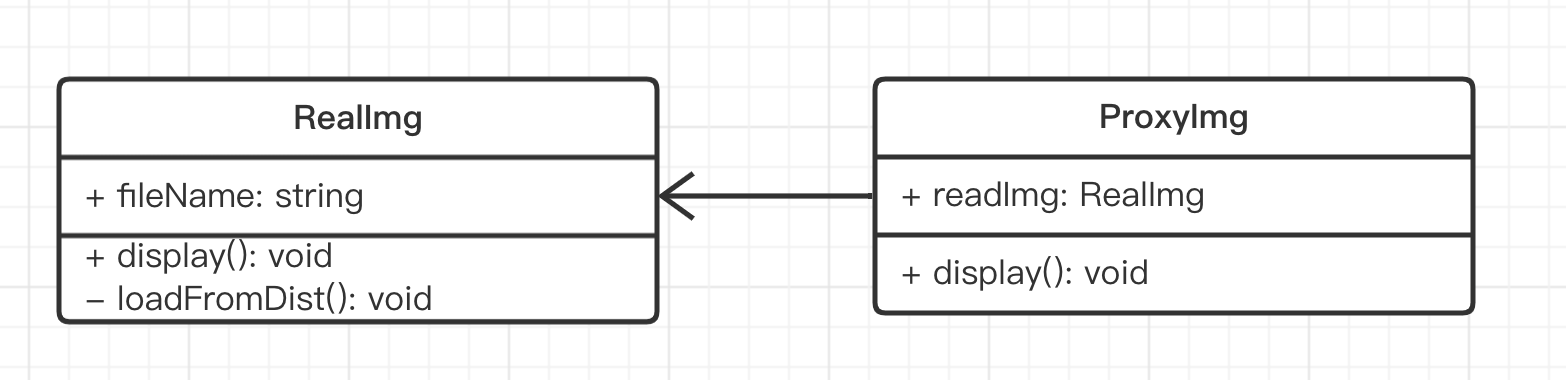
ts
class RealImg {
fileName: string
constructor(fileName: string) {
this.fileName = fileName
this.loadFromDist()
}
display() {
console.log('display...', this.fileName)
}
private loadFromDist() {
console.log('loading...', this.fileName)
}
}
class ProxyImg {
readImg: RealImg
constructor(fileName: string) {
this.readImg = new RealImg(fileName)
}
display() {
this.readImg.display()
}
}
const proxImg = new ProxyImg('xxx.png') // 使用代理
proxImg.display()是否符合设计原则?
5 大设计原则中,最重要的就是:开放封闭原则,对扩展开放,对修改封闭
- 代理和目标分离,解耦
- 代理可自行扩展逻辑
- 目标也可自行扩展逻辑
场景
代理模式在前端很常用
DOM 事件代理
html
<div id="div1">
<a href="#">a1</a>
<a href="#">a2</a>
<a href="#">a3</a>
<a href="#">a4</a>
</div>
<button>点击增加一个 a 标签</button>
<script>
var div1 = document.getElementById('div1')
div1.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
var target = e.target
if (e.nodeName === 'A') {
alert(target.innerHTML)
}
})
</script>webpack devServer
第一,配置 webpack ,参考 https://webpack.docschina.org/configuration/dev-server/#devserverproxy
js
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
// 其他配置...
devServer: {
proxy: {
'/api': 'http://localhost:8081',
},
},
};第二,启动 nodejs 服务,监听 8081 端口
第三,借用 axios 发送请求
ts
import axios from 'axios'
document.getElementById('btn1')?.addEventListener('click', () => {
axios.get('/api/info')
.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
})nginx 反向代理
nginx 配置文件可参考 https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/nginx-setup-intro.html
nginx
server {
listen 8000;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8001;
}
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8002;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}Proxy
Vue3 就使用 Proxy 做 data 响应式
ts
// 明星
const star = {
name: '张三',
age: 25,
phone: '18611112222',
price: 0 // 艺术物价,明星不谈钱
}
// 经纪人
const agent = new Proxy(star, {
get(target, key) {
if (key === 'phone') {
return '13900001111' // 返回经纪人的的电话
}
if (key === 'price') {
return 100 * 1000 // 报价
}
return Reflect.get(target, key) // 返回原来的属性值
},
set(target, key, val): boolean {
if (key === 'price') {
if (val < 100 * 1000) {
throw new Error('价格太低了...')
} else {
console.log('报价成功,合作愉快!', val)
return Reflect.set(target, key, val)
}
}
// 其他属性不可设置
return false
}
})
// 主办方
console.log(agent.name)
console.log(agent.age)
console.log(agent.phone)
console.log(agent.price)
// agent.price = 90000 // 价格低了会报错Proxy 的使用场景
跟踪属性访问
Vue3 就是通过这个特性实现数据响应式
ts
const user = {
name: '张三'
}
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, key) {
console.log('get...')
return Reflect.get(target, key)
},
// get(...args) {
// return Reflect.get(...args)
// },
set(target, key, val) {
console.log('set...', val)
return Reflect.set(target, key, val)
}
})
proxy.name = '李四'
console.log(proxy.name)隐藏属性
ts
const hiddenProps = ['girlfriend'] // 要隐藏的属性 key
const user = {
name: '张三',
age: 25,
girlfriend: '小红'
}
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, key) {
if (hiddenProps.includes(key as string)) return undefined
return Reflect.get(target, key)
},
has(target, key) {
if (hiddenProps.includes(key as string)) return false
return Reflect.has(target, key)
},
set(target, key, val) {
if (hiddenProps.includes(key as string)) return false
console.log('set...', val)
return Reflect.set(target, key, val)
}
})
console.log('age', proxy.age)
console.log('girlfriend', proxy.girlfriend) // undefined验证属性
如果用 TS ,会有静态类型检查,用不到这个验证。用 JS 的话会有效果。
以下代码可以在浏览器中运行(非 TS 环境)
ts
const user = {
name: '张三',
age: 25,
}
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {
get(target, key) {
return Reflect.get(target, key)
},
set(target, key, val) {
if (key === 'age') {
if (typeof val !== 'number') return false // 验证 age 类型
}
return Reflect.set(target, key, val)
}
})
proxy.age = 'a'
console.log(proxy.age) // 25记录实例
ts
const userList = new WeakSet() // 每次初始化 user ,都记录到这里
class User {
name: string
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name
}
}
const ProxyUser = new Proxy(User, {
construct(...args) {
const user = Reflect.construct(...args)
userList.add(user) // 记录 user 对象
return user
}
})
const user1 = new ProxyUser('张三')
const user2 = new ProxyUser('李四')
console.log('userList', userList)Proxy 的注意事项
捕获器不变式
这是“红宝书”里的叫法。捕获器即 get ,不变式即不能因为 Proxy 而改变对象本身的描述符特性。
ts
const obj = { x: 100, y: 0 }
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'y', {
value: 200,
writable: false,
configurable: false,
})
const proxy = new Proxy(obj, {
get() {
return 'abc'
}
})
console.log(proxy.x)
console.log(proxy.y) // y 属性描述符被修改,proxy 不能修改它的值this
函数里的 this 是由执行时确认的,而非定义时。
ts
const user = {
name: '张三',
getName() {
console.log('this...', this)
return this.name
}
}
const proxy = new Proxy(user, {})
user.getName() // 执行时 this 是 user
proxy.getName() // 执行时 this 是 proxy